Only the lazy person doesn't talk about soft skills. Some say that people with soft skills are more promising than people with specialized skills. Whether this is true or not, we will figure it out.
What are soft skills anyway
Soft skills or soft skills are universal skills that reflect your personal qualities, how well you can:
- to interact with the public,
- to learn quickly,
- respond to force majeure in a timely manner,
- work in conditions of complete uncertainty and so on.
Soft skills are needed by everyone, regardless of their position, specialty or status. They affect any human activity, but they are not directly related to any of the professions. In an unfamiliar environment, any untrained person, whether they are a sales Manager or an oil magnate, will be confused. And you, having soft skills, can adapt to the situation.
There are also hard skills: the degree of tool ownership, driving experience, language proficiency and so on. These skills are hard for a reason, within a certain specialty, they are quite same. But with soft skills, everything is not so - in some situations, you will need different skills, regardless of your specialty.
What soft skills are there
There are more than 60 soft skills in total. To list them all, no article is enough, so I will tell you only about the most useful and popular.
I like to divide soft skills into universal (everyone needs them) and managerial (managers need them). Universal skills are related to your personal effectiveness and interaction with other people. And managerial... well, with management. If you divide the most important soft skills into these groups, you get this.
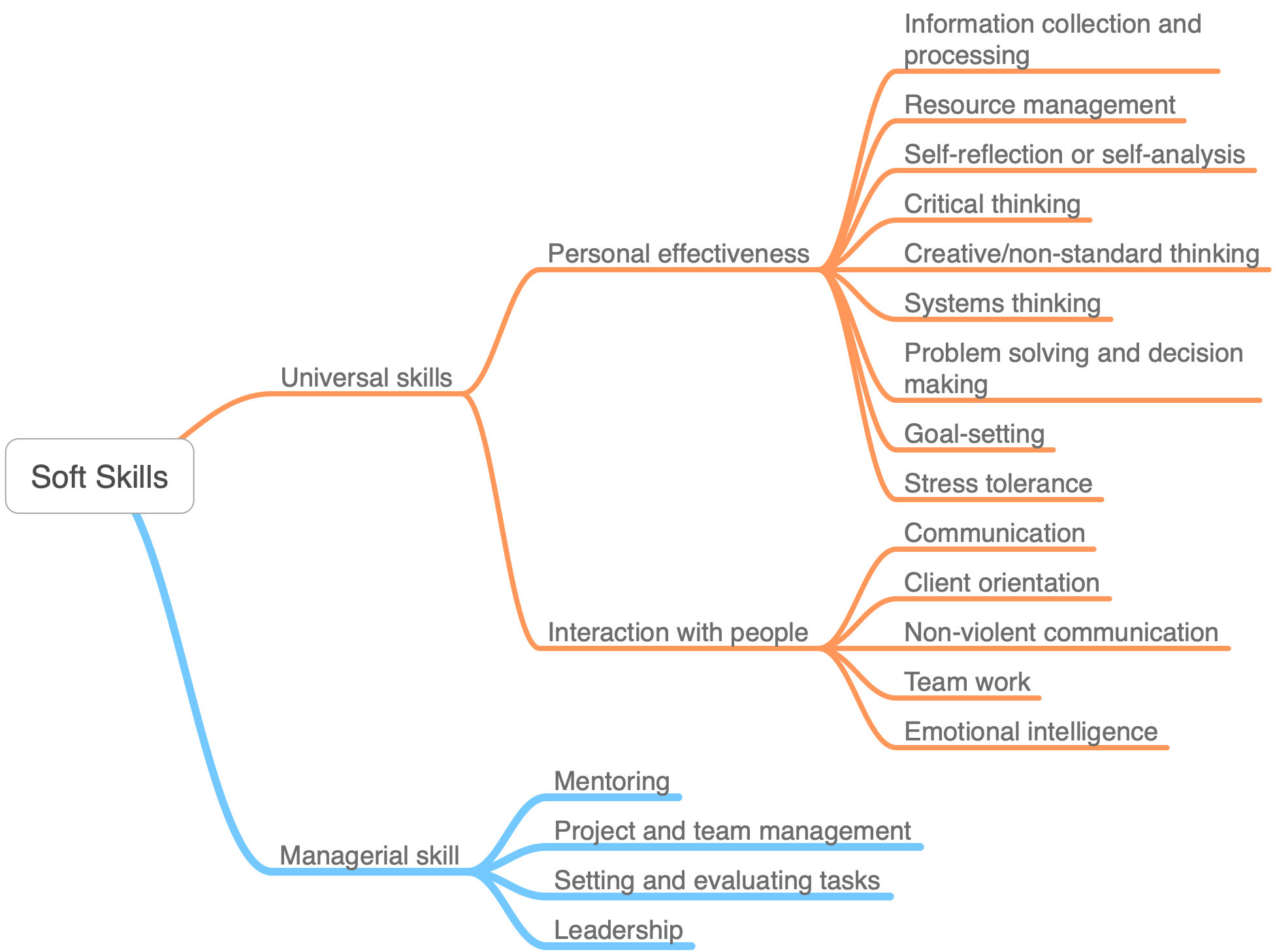
Universal skills
Personal effectiveness
Information collection and processing - the most important skills of any modern person. The ability to ask the right questions, work with information and share it with others is useful at the training stage and at the stage of solving any work tasks.
Resource management. Time is your main resource. We live and work at a high pace, so it is very important to be able to manage it correctly.
Self-reflection or self-analysis — the ability to look at yourself from the outside, evaluate your actions and decide what to do next. Useful when you can't find a common language with colleagues.
Critical thinking - ability to consume and process information in a balanced manner, check facts, and think rationally. It helps not to get lost in the information flow, not to become a victim of manipulation, and to prove your point of view in a reasoned manner.
Creative/non-standard thinking. Only by moving away from the generally accepted schemes and templates, you can create something truly new. This is a very valuable skill for any specialist who not only wants to be competitive, but also wants to leave their mark on history.
Systems thinking — the ability to analyze complex objects, dig into details, find relationships and be able to look at the object of analysis from the outside. Thanks to this skill, you understand how something works, and, if necessary, you can create this "something" yourself.
Problem solving and decision making. These are actually two skills, but they are very close. Thanks to them, you can choose the best solution possible, take measures and cope with difficulties in order to achieve the goal and get results.
Goal-setting - the ability to formulate and set goals for yourself or others. If you set the goal correctly, you will immediately understand the criteria for achieving it.
Stress tolerance - the ability not to lose effectiveness under heavy loads and calmly treat conflict situations. At work, this is generally an indispensable skill, especially in IT, where processing is often within the norm.
Interaction with people
Communication - communication skills in their global understanding. Speaking about communication, they mean not just the exchange of information and knowledge, but also a lot of other things: the ability to negotiate and find a common language, summarize the results of a conversation, establish oral agreements, read the situation and so on.
Client orientation - ability to determine the client's wishes and needs in a timely manner. For example, now customer-oriented companies have launched services for delivering food and other goods to your home. People feel taken care of - companies get loyal customers. It's a cool skill that helps you compete.
Non-violent communication - a skill that allows you to clearly and clearly achieve your goals from the other person. Instead of making demands and manipulating, you report a fact-based observation and formulate a request. In general a good fellowship,
Team work - ability to delegate work in certain situations. It seems simple, but in fact this is a real problem - it is easier for many people to do the work themselves than to achieve results from a colleague for a long time.
Emotional intelligence - the ability to recognize and express emotions (your own and others), manage them, talk about them, notice them in time and use them to complete your tasks. Emotional intelligence and communication skills help you negotiate.
Managerial skill
Mentoring - the ability to share knowledge, skills and abilities with other people and control their learning process. An important quality of a manager who recruits newcomers to the team.
Project and team management. Projects are everywhere: in your personal life and at work. Organize an event, make a website, make repairs in the apartment - all these projects. You are at the center of the project, as a manager, and around you are clients, contractors, colleagues, and so on. In order for a project to be cool, you need to be able to plan your work, interact with the team and monitor its activities.
Setting and evaluating tasks. In order for the work to move at the right pace and in the right direction, you need to be able to correctly assess the cost of resources and set tasks. By the way, if most people have learned to set tasks plus or minus, then everything is not very good with the assessment. So, if you learn, my respect.
Leadership - the ability to rally like-minded people around you and lead the team to success. This is an important skill not only for politicians, but also for any top managers. Ideally, a company director should be not just a manager, but also a team leader.
Why do you need them
Knowledge becomes outdated, but skills don't. Especially universal ones like soft skills. And now, to be a competitive cadre, it is not enough to get professional knowledge. You need to be able to quickly adapt to new conditions and look for non-standard solutions.
In general, the ratio of hard and soft skills depends on the company and position. For example:
- For a scientist or nuclear physicist, professional skills are more important than universal ones.
- For professionals who work with people, it is important to maintain a balance. Lawyers or accountants should be friendly, organized and patient professionals.
- For creative professions, sales or business, soft skills clearly prevail over hard. Even without special education, you can get decent clients. All thanks to the ability to speak, listen, win over the interlocutor, speak publicly and so on.
In short, soft skills are the competencies of the future. In one of the following articles, I will explain in detail how to develop them using books and courses.