In our articles, we have repeatedly touched on project management: we talked about methodologies (Waterfall, Agile), and about methods (Scrum), and about methods. But if the problem is within the project - for example, a defective product or dissatisfied customers - you need to look for an error in the processes themselves. There are special process management methodologies for this. Let's continue to study the issue and deal with another methodology with the unusual name of Six Sigma.
6 sigma concept
The Six Sigma methodology considers all defects, shortcomings and limitations in general, without focusing on one thing (as the theory of constraints does). In accordance with it, it is important to reduce the total number of defects at all stages of work and the possibility of their occurrence in the future.
In a Six Sigma project, numbers and exact metrics are important, and any decision is thoroughly tested - nothing can be done based on inaccurate information. And employees in such a project are arranged in a hierarchy according to the color of the “belt”. But more on that later.
Let's first understand what sigma is. This word comes from the theory of probability, where it denotes the sign of an error or deviation from a normal value.
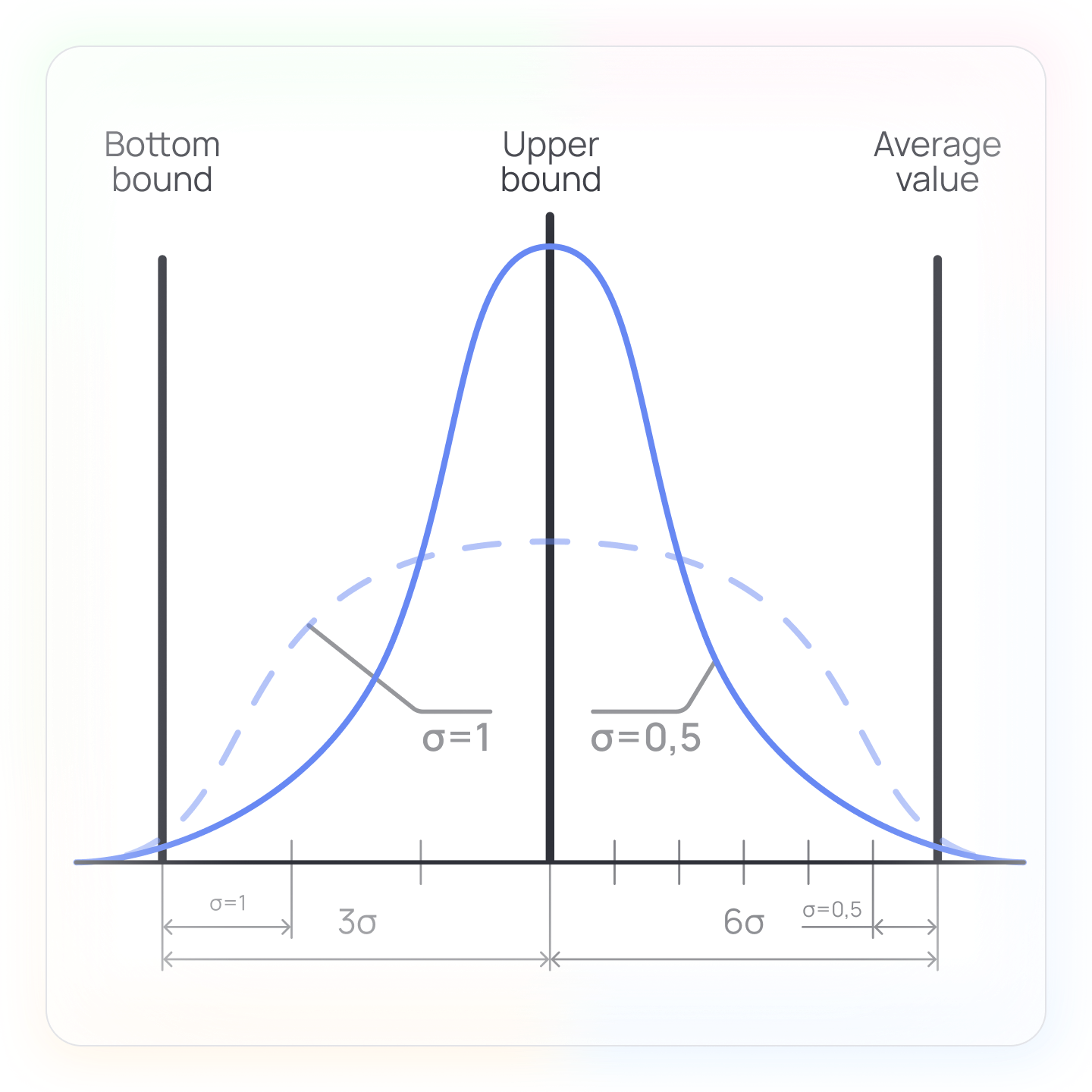
If we talk about processes, or rather about their quality parameters, then using the deviation (sigma) and the average value, we can estimate the proportion of defects in them. To do this, you need to set the upper and lower tolerance limits, and see how many sigmas fit between the average value and any of the limits. If 6 sigma is met, the number of defective results at the output of the process will be at the level of error - 3.4 per 1 million.
The idea of the Six Sigma methodology is to reduce the standard deviation (sigma) in the tolerance field in various ways. More tolerance field means more quality results at the output of the process. More sigma value - less qualitative results.
History
Six Sigma was invented by a Motorola engineer in the 1980s when there were too many manufacturing defects and something needed to be done about it. The methodology was used to fix internal problems and minimize the number of defective results.
Later it was taken over by other companies. In the 1990s, Jack Welch of General Electric made Six Sigma one of the company's key operating strategies. The methodology began to be used not only to reduce marriage, but also to find any shortcomings at all stages of work and reduce the likelihood of their occurrence.
Principles of 6 Sigma
- Value for the consumer. When managing processes, it is important to listen to the customer's opinion and eliminate any product flaws. What is of no value to him is useless.
- Team motivation. Employees must be involved in the process and focused on achieving results. To make the project attractive to them, take into account their opinion and do not turn a blind eye to dissatisfaction. Higher team engagement means better product quality.
- Eliminate inefficient processes. It is necessary to evaluate the quality of the product from the client side - this way you can notice inefficient processes that are not worth spending resources on. They need to be eliminated, changed or simplified. The main thing is to satisfy the needs of the end user.
- Setting measurable goals and process indicators. Only accurate data matters. All goals and expected results must be measurable so that data can be collected, analyzed and improvements made.
- Making decisions based on accurate data. When making any decision on the project, operate with facts, not assumptions and conjectures.
How to implement
There are two algorithms for implementing the 6 Sigma methodology - the choice depends on the stage at which the product is:
- if it starts - the DFSS algorithm,
- if it already works and you need to change something - the DMAIC algorithm.
DFSS
An algorithm used for new projects that need to enter the market with established processes. Implemented in five stages:
- Determination of precise goals, problems of the target audience and key indicators for achieving the goals.
- Measurement - Selecting data and evaluating it.
- Analysis of information, causes of defects and determination of relationships.
- Design - search and selection of the best solutions, their implementation.
- Monitoring the results and managing the processes of work on the product.
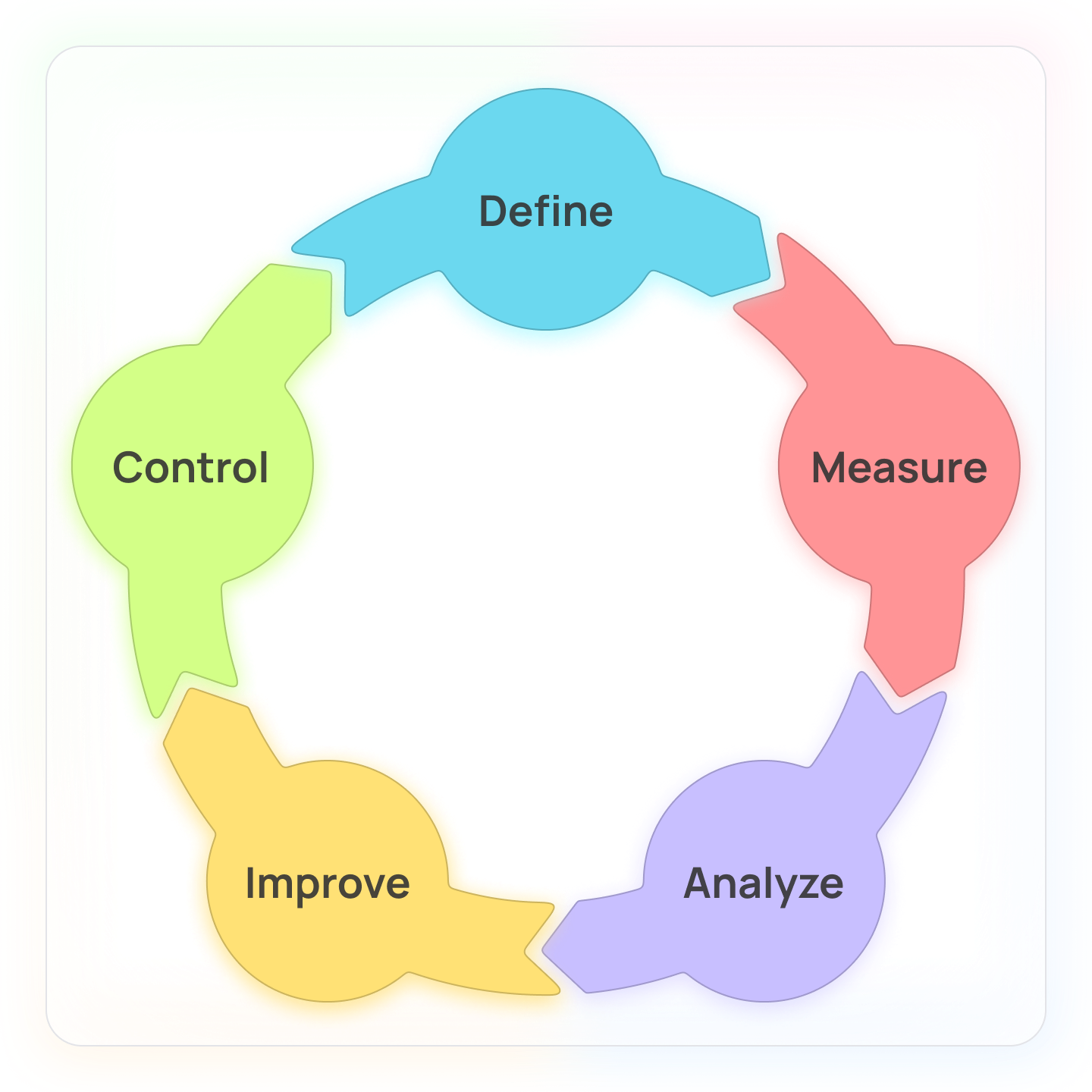
DMAIC
The algorithm is suitable for existing projects that have shortcomings. Helps optimize quality and improve performance. It also consists of five stages:
- Definition the goals of the project and the needs of consumers.
- Measurement the available process data.
- Analysis defects, customer reviews and employee feedback, the causes of deficiencies.
- Improvement the process through the search for new solutions, their implementation.
- Control of the further work of the product, management.
Tools
When managing processes, you need to be aware of any shortcomings even before receiving feedback from customers or employees. There are several ways to do this:
- "5 Whys". Ask the question "Why?" in any difficult situation until you get to the bottom of the answer.
- Payback. If there are several solutions, choose the one that benefits more than the costs.
- Mind cards. Create a map of all processes to see all the stages of work and understand where there may be shortcomings.
- Diagrams and analysis. Data and information is more convenient to visualize using charts and analyze to find errors in processes.
Hierarchy of control
Six Sigma involves the involvement of all employees, including project managers. Depending on the position and skills, they are clearly divided into categories according to “belts”. Yes, like karate.
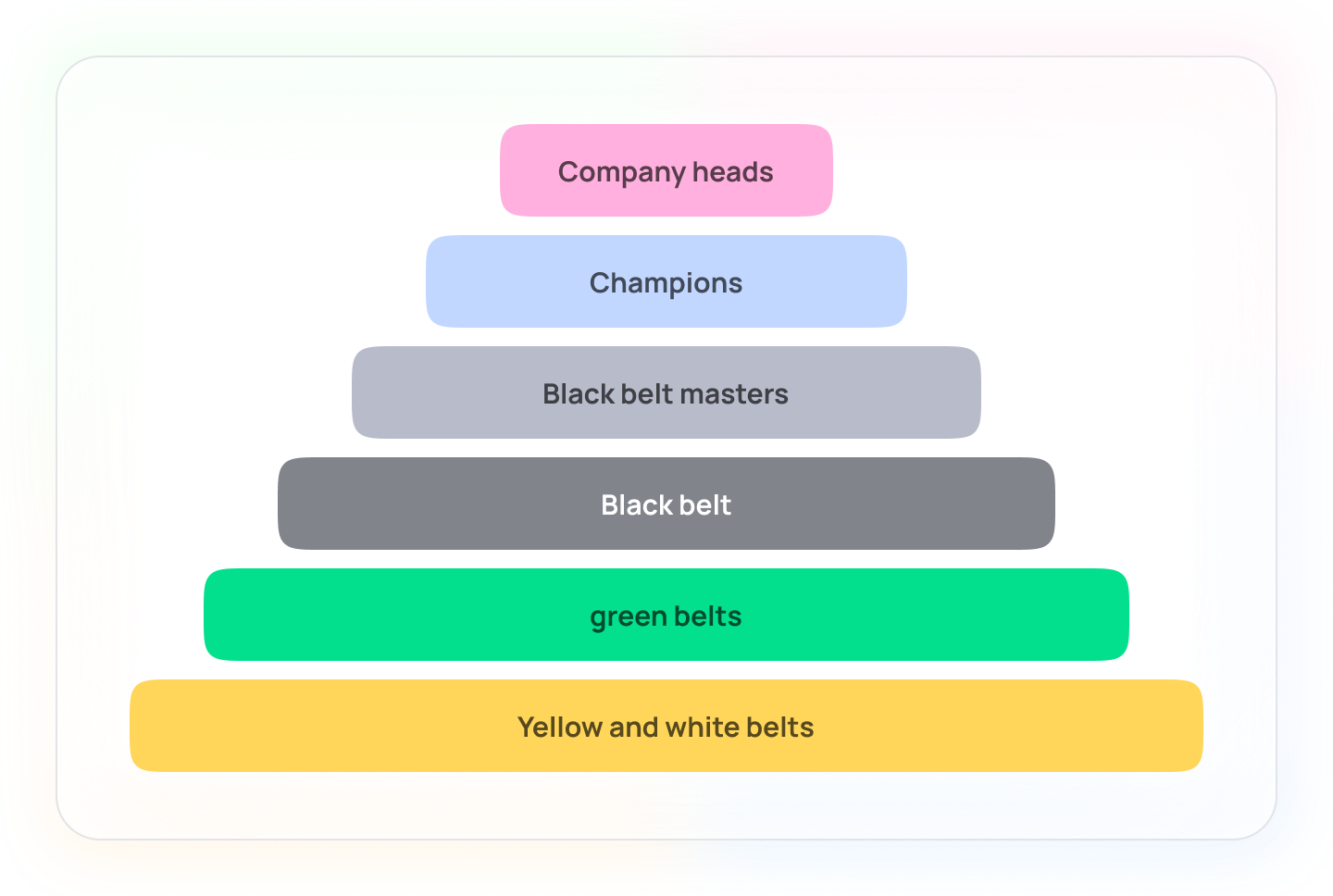
- The head of the company is the leader. He makes responsible decisions, distributes tasks, motivates and involves employees in the process.
- Champions implement methodology and mentor Black Belts.
- Black Belt Masters supervise Black Belts, distribute tasks.
- Black Belts work on tasks under the guidance of Masters.
- Green belts carry out their tasks and monitor the quality of processes.
- Yellow and white belts are familiar with the internal processes at the initial level, most often they are interns and juniors.
Advantages and disadvantages
The difference with 6 Sigma is that it is characterized by increased control over processes and the improvement of complex defects. Consider why you should implement Six Sigma in your business:
- Versatility. The 6 Sigma methodology is suitable for any projects and processes.
- Focus on clear results. Engaged employees and precise goals increase the chances of successful implementation.
- Minimizing the appearance of defects. The methodology does not focus on a single process, it is important here to minimize the possibility of any defects.
But at the same time, Six Sigma limits creative freedom - all results are tied to numbers and are limited by rigid frameworks that make it impossible to develop ideas and hypotheses and quickly test because of a clear plan.